Your Unified Data Security Platform
ALTR delivers the simplest way to unify, secure, and govern data access across your modern data stack.
Operate, accelerate and scale with confidence.
Control
Enforce policies and protect sensitive data across your cloud ecosystem—confidently, consistently, and at scale.
Empower
Enable teams to access governed data on their own—securely, independently, and without delays.
Innovate
Empower AI innovation through secure, policy-driven access so your teams can build with confidence.
Powerful Cloud Data Security, Zero Compromise




One Platform for Multi-database Support
Manage and secure data across multiple databases from a single, unified data security platform, reducing complexity and improving efficiency.
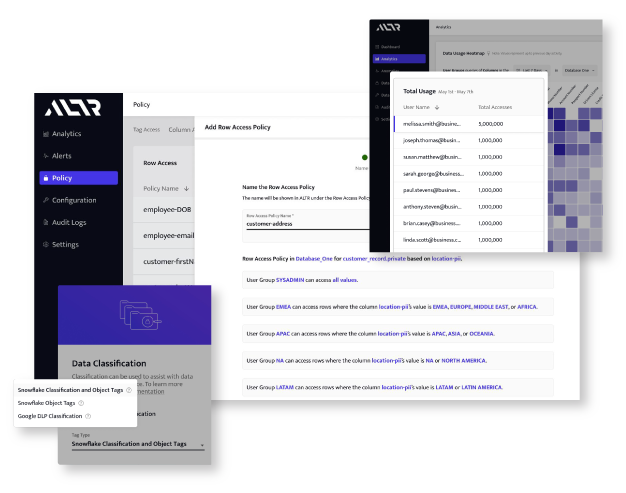
Centralized Policy Management
Create, enforce, and monitor data access policies from a single dashboard—streamlining governance, ensuring consistency, and reducing risk.
Compliance-Ready Data Protection
Ensure your data security practices meet regulatory standards with advanced data protection like tokenization and format-preserving encryption.
Real-time Database Activity Monitoring
Gain real-time visibility into data usage, empowering you to detect, neutralize and report unauthorized access before it escalates into a threat.
Automated Data Discovery
No DIY Complexity
Eliminate manual SQL and custom coding with automated controls—saving time, reducing errors, and enhancing data protection.
"ALTR significantly contributes to organizations’ ability to tightly control and monitor data access, capturing the essence of zero-trust security models, where data access is never assumed to be safe and is always verified and closely monitored. This makes it a cool choice for organizations looking for a data security platform." - Gartner

Protect What Matters While You Build What’s Next.
Modern organizations need to move fast—but not at the expense of data security. Whether you’re migrating to the cloud, collaborating with partners, or testing in non-prod environments, ALTR keeps your sensitive data protected at every step.
Get started with ALTR’s Data Security Platform
Secure Data Cloning
Clone production datasets for non-production use—without exposing PCI, PII, PHI, or regulated data. With ALTR, sensitive fields stay masked or tokenized, giving developers and analysts the access they need without compromising security or compliance.
Secure Data Sharing
Share governed data with third parties, vendors, or partners while retaining complete visibility and control. ALTR enforces masking, access policies, and audit trails, ensuring shared data stays protected and compliant—no matter where it goes.
Secure Cloud Migration
Lift and shift without risk. ALTR applies format-preserving encryption (FPE) and access controls during your cloud migration process, so sensitive data stays secure from day one. Avoid manual rework, reduce complexity, and meet compliance requirements faster.
CASE STUDIES
Real solutions, real results.

























From cloud warehouses to security tools, we partner with industry leaders so your data can go further, faster—without compromising compliance.
GET STARTED
Start Securing Your Data in Minutes with ALTR
Get started with ALTR’s Data Security Platform